Data Recovery -> RAID 3
Storage devices
Types of HDD
Partition Series
Linux
Operating Systems
Windows
RAID 3
What is RAID 3?
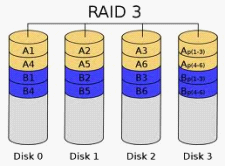 RAID 3 divides the data into several blocks and stores them in N+1 disks through corresponding Fault Tolerant algorithm. The available space taken up by actual data is total capacity of N disks. And the data stored in the N+1 disk is Fault-tolerant calibration information. In a disk array, the possibility that more than one disk fail at the same time is very small. So RAID 3 can guarantee the system security normally. Compared with RAID 0, read-write speed of RAID 3 is slower. The applications of RAID depend on Fault Tolerant algorithm and size of block. In conventional practice, RAID 3 is suitable for large file s and applications demanding higher security, for example, video editing, disk broadcast, large database and so on.
RAID 3 divides the data into several blocks and stores them in N+1 disks through corresponding Fault Tolerant algorithm. The available space taken up by actual data is total capacity of N disks. And the data stored in the N+1 disk is Fault-tolerant calibration information. In a disk array, the possibility that more than one disk fail at the same time is very small. So RAID 3 can guarantee the system security normally. Compared with RAID 0, read-write speed of RAID 3 is slower. The applications of RAID depend on Fault Tolerant algorithm and size of block. In conventional practice, RAID 3 is suitable for large file s and applications demanding higher security, for example, video editing, disk broadcast, large database and so on.
Disadvantages of RAID 3
Apart from the disadvantages about data writing and degraded mode discussed previously, other defects should be also paid attention to in the application of RAID 3. The greatest weakness of RAID 3 is that calibration disk is prone to bottleneck of the whole system, which is why it is hardly adopted by users.
It is known that data writing operations are scattered into several disks by RAID3. No matter which disk are the data written in, related information in calibration disk must be re-written. However, because of the applications needing more writing operations, the load of f calibration disk is very big. Therefor, it can not meet the demand for program speed and the whole RAID system performance descends. For this, RAID 3 is suitable for the condition that writing operation is less and read operation is more such as database and WEB server.
 RAID 3 divides the data into several blocks and stores them in N+1 disks through corresponding Fault Tolerant algorithm. The available space taken up by actual data is total capacity of N disks. And the data stored in the N+1 disk is Fault-tolerant calibration information. In a disk array, the possibility that more than one disk fail at the same time is very small. So RAID 3 can guarantee the system security normally. Compared with RAID 0, read-write speed of RAID 3 is slower. The applications of RAID depend on Fault Tolerant algorithm and size of block. In conventional practice, RAID 3 is suitable for large file s and applications demanding higher security, for example, video editing, disk broadcast, large database and so on.
RAID 3 divides the data into several blocks and stores them in N+1 disks through corresponding Fault Tolerant algorithm. The available space taken up by actual data is total capacity of N disks. And the data stored in the N+1 disk is Fault-tolerant calibration information. In a disk array, the possibility that more than one disk fail at the same time is very small. So RAID 3 can guarantee the system security normally. Compared with RAID 0, read-write speed of RAID 3 is slower. The applications of RAID depend on Fault Tolerant algorithm and size of block. In conventional practice, RAID 3 is suitable for large file s and applications demanding higher security, for example, video editing, disk broadcast, large database and so on.Disadvantages of RAID 3
Apart from the disadvantages about data writing and degraded mode discussed previously, other defects should be also paid attention to in the application of RAID 3. The greatest weakness of RAID 3 is that calibration disk is prone to bottleneck of the whole system, which is why it is hardly adopted by users.
It is known that data writing operations are scattered into several disks by RAID3. No matter which disk are the data written in, related information in calibration disk must be re-written. However, because of the applications needing more writing operations, the load of f calibration disk is very big. Therefor, it can not meet the demand for program speed and the whole RAID system performance descends. For this, RAID 3 is suitable for the condition that writing operation is less and read operation is more such as database and WEB server.